Unveiling the Raw Materials and Composition of Channel Glass
2024-04-30
In the contemporary realm of building materials, the application of Channel Glass has seen a growing prevalence. Contrasted with traditional ordinary glass, Channel Glass boasts features such as light transmission without distortion, aesthetic appeal, and heightened strength. So, what raw materials are requisite for Channel Glass production, and what roles do these materials fulfill? Let's delve into each facet.
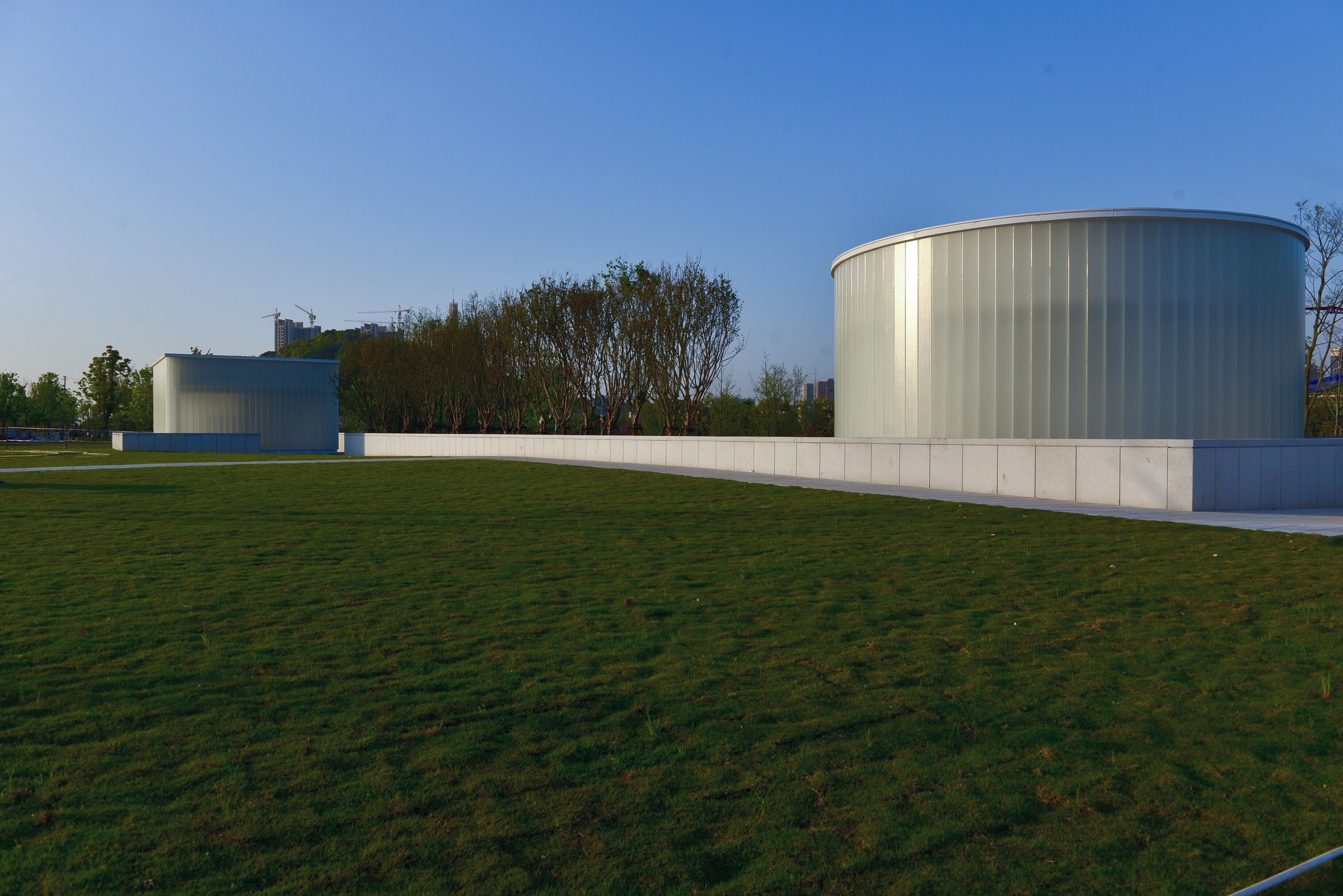

Appleton Channel Glass Project: Park in Changsha City
Firstly, let's scrutinize the molecular structure of Channel Glass.
Liquid State
When subjected to high-temperature heating, a piece of Channel Glass gradually transforms into a liquid state, as illustrated in the diagram.
Crystal State
Post a gradual cooling process following the melting of Channel Glass, crystallization occurs, inducing a shift in the molecular structure, eventually giving rise to crystals. It's imperative to note that these crystals deviate from the desired glass state.
Glass State
To revert the liquid glass to the customary glass state, swift cooling becomes imperative. After such rapid cooling, the molecular structure realigns into a state between liquid and crystal, forming what we commonly refer to as glass.
As evident, glass isn't the solid or liquid encountered in our daily lives; it assumes a peculiar semi-solid semi-liquid state with a very sluggish flow rate. Hence, temperature mastery is pivotal in the glass-making process.
Now, let's proceed to the composition and raw materials of Channel Glass. Typically, Channel Glass is predominantly composed of four primary elements.
1. Basic Components
Resembling most ordinary glass, the fundamental chemical constituents of Channel Glass encompass silica dioxide, sodium oxide, calcium oxide, and magnesium oxide.
Silica dioxide, sourced from quartz sand, serves as the primary glass component, renowned for its exceptional durability. However, using it alone proves challenging due to its high melting point.
Low iron Sand
To mitigate the melting point of quartz sand, sodium oxide is introduced. Yet, the presence of sodium ions renders it chemically reactive. In industrial applications, soda ash provides a significant supply of sodium oxide.

Soda Ash
Calcium oxide stands as another crucial element augmenting glass durability. However, at elevated temperatures, it can induce crystallization, affecting light transmission. Limestone and dolomite host substantial amounts of calcium oxide.
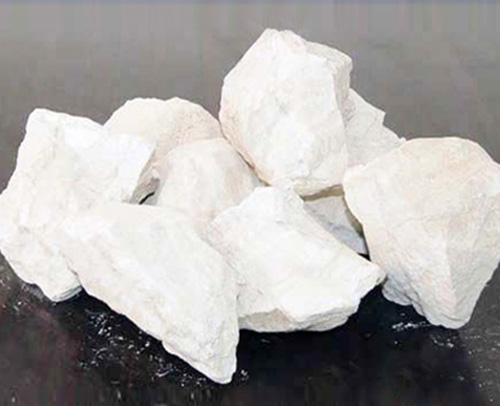

Limestone
To counter this issue, magnesium oxide is frequently introduced to impede crystallization at high temperatures. Dolomite contributes a significant supply of magnesium oxide.

Dolomite
These four elements constitute the fundamental components of most glass, yielding what is commonly known as soda-lime glass.
2. Trace Components
In addition to the aforementioned basic elements, Channel Glass may incorporate additives as required. Most commonly utilized is aluminum oxide, effectively enhancing the glass's moisture resistance. When producing clear Channel Glass, the inclusion of iron red powder can effectively eliminate bubbles resulting from factors like carbon dioxide in the raw materials, rendering the glass clearer. However, iron red powder imparts color to the glass, prohibiting its use in ultra-clear Channel Glass raw materials.


Aluminum Oxide and Iron Oxide
Furthermore, the addition of oxidizers can bestow greater crystal clarity upon the glass. If specific requirements dictate, suitable amounts of coloring agents, such as cobalt, selenium, nickel, etc., can be introduced to alter the glass's color.
3. Clarifying Agent
In industrial production, a measured amount of saltpeter is added as a clarifying agent, effectively expelling gases like carbon dioxide contained within the liquid glass, rendering the glass clearer.

Sodium Sulfate
4. Cullet
The introduction of cullet into the raw materials aims to effectively lower the melting point, facilitating the processing of raw materials.

Cullet
Thus, based on requirements, the aforementioned four types of materials are weighed and blended in varying proportions, conveyed into the furnace, and, through processes like product formation, annealing, cooling, and cutting, the final Channel Glass is attained.
In industrial applications, additional processing techniques such as tempering, sandblasting, high-temperature glazing, etc., can be applied to achieve the desired usage effects.
Channel Glass








